Mauritania Eco Resort & Spa
Mauritania Eco Resort & Spa
Tuilit, Mauritania
LOCATION
Tuilit, Mauritania
Project Facts
Project Mauritania Eco Resort and Spa
Client ASML Group
Built-Up-Area N/a
Services Tourism Studies, Feasibility Studies, Master Planning, Architectural Concept and Preliminary Design, Landscape Preliminary Design, 3D Rendering
Status Detail Design
Budget US$120 million
Project Features
Guest Accommodation comprising 30 Guest Suites (combination of Standard and Executive).five Family Suites and two Presidential Suites.
Main Palace housing Guest Check-in, the Grand Hall, Male Majlis, Female Majlis, Retail Outlets, Cigar Bar, Pre-dinner Drinks Bar, three specialty Restaurants supported by three commercial kitchens, a Library, Meeting Rooms, and Admin Areas.
Multipurpose Venue/ Conference Centre with MICE facilities housing a large ballroom capacity of 350 banquet style seating, meeting rooms, a boardroom.
Day Spa with Men’s and Ladies’ separate Hammams and Massage facilities including eight single Treatment Rooms.
Recreational Facilities comprise four Swimming Pools including separate Ladies only pool and a Men’s only pool, a Pool bar, Pool Terraces, and Guest Beach.
The Mauritania Eco Resort and Spa will be located between the capital city of Nouakchott and some 300 kilometres from the Banc d’Arguin National Park in an area known as Tiouilit; 170 kilometres from the town of Nouadhibou, 400 kilometres from Chinguetti and 150 kilometres from Nouakchott International Airport.The site is a beachfront location characterised by its rocky outcrops facing the sea. Surrounded on three sides by sweeping sand dunes, the fourth side is hemmed by a one kilometre of pristine coastline.
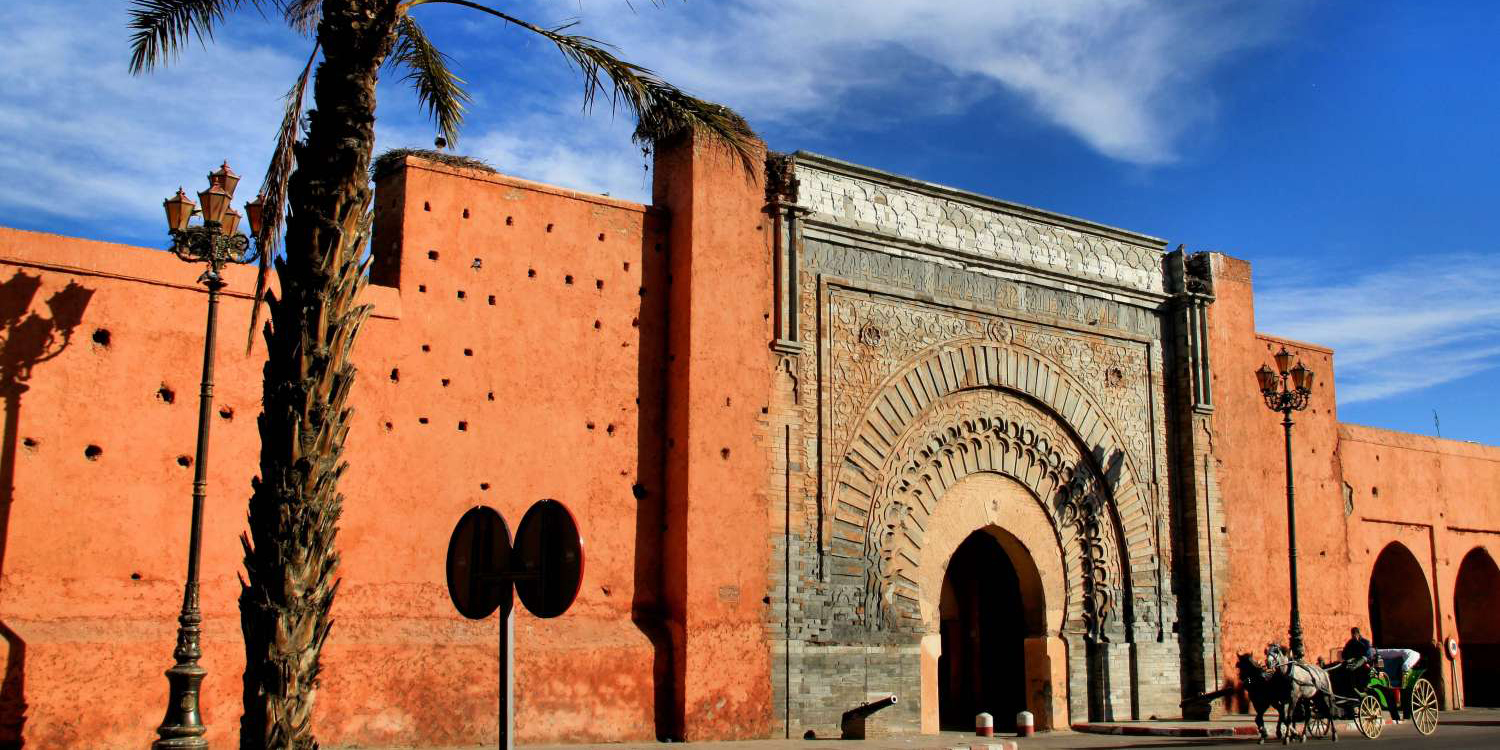
The 800-kilometre coast line of Mauritania is devoid of any such cities or towns and consequently there is no real noteworthy architecture to preserve. This presented somewhat of a challenge for the designers and development team as there are no architectural references to draw from. Each of the Ksours has a distinct architectural heritage resulting from its rich history, so to use any one style at the resort would also be wrong as the coastal location of the development has no direct relevance to the history of these cities. Similarly, to simply emulate an architectural typology would result in a development that resembles what has already been persevered – another living museum.
Successful architecture is one that links to time and place. Hence, the task for the designers will be to create a development which, while being firmly rooted in Mauritania sensitively integrates modern-day technologies and techniques to offer world-class service and accommodation; and to ensure it too does not suffer the same fate as the architectural marvels of their time at Chinguetti, Oualata, Ouadane and Tichitt.


Almoravids
The Neo-Mauritanian Style
The cradle of the Almoravid movement, which spread Islam throughout the region and even controlled Spain for a short period, Mauritania gained independence from France in 1960. Covering an area of 1.04 million sq. metres (398,000 sq. miles) its population is count according to the UN in 2009 was only 3.3 million.
The Islamic Republic of Mauritania bridges the Arab Maghreb and the western sub-Sharan Africa; a largely-desert country, it presents a cultural contrast between an Arab population to the north and black Africans to the south. Threatened by desertification, the country has a rich architectural and cultural history which offers tourists unmatched experiences anywhere in Africa, the Middle East or Europe.
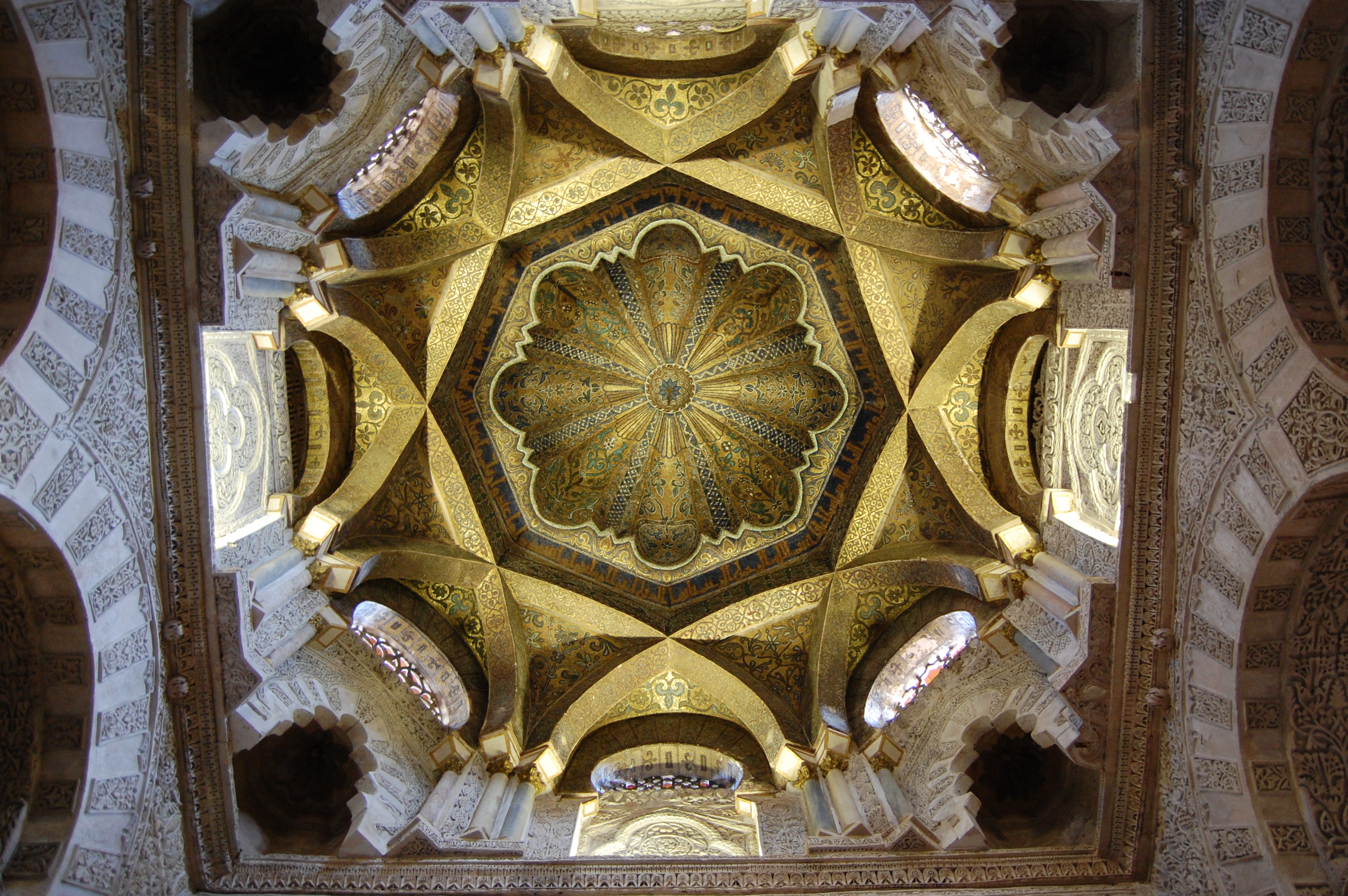
The architectural and interior design of the development consequently relies on the history of Mauritania, and tries to draw on its influences today as well as the past. Taking references and clues from the past, these are developed to bring them up to today’s standards through a process of ‘adopt and adapt’ – a style we refer to as the ‘Neo-Mauritanian’ style.
The ‘Neo-Mauritanian’ style was coined by Mr Rashid Taqui when faced with the challenge of defining the architectural style of the eco resort and edutainment complex that spoke of identity. Research showed that Mauritania had a rich cultural and architectural legacy, with four UNESCO- preserved cities today, each with its own unique architectural style. Scattered across the vast territory of Mauritania, it was considered inappropriate to merely copy one or all of the styles. So a study was undertaken by Mr Taqui to understand the principles of the spaces, their hierarchy inter-relationship and the historical influences that lead to such manifestations.

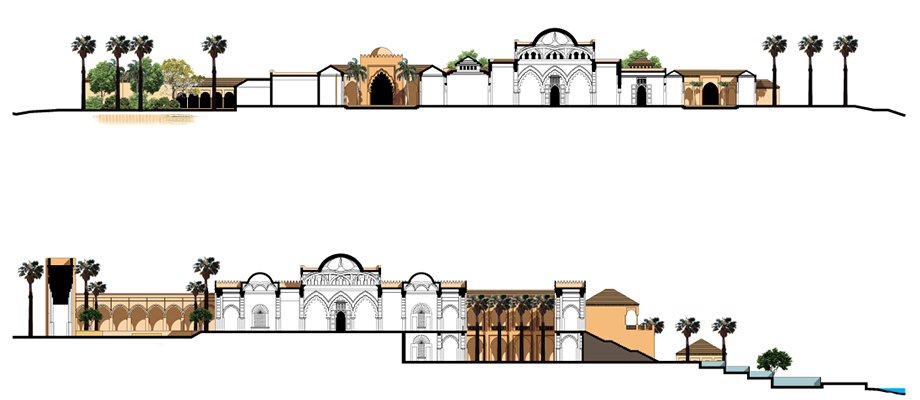
Outcomes of this research highlighted common threads among each and combined with the general history of Mauritania, commonality was found between architectural developments in parts of Spain, and the Maghreb region including the countries Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia historical architecture of the Maghreb region shows a more refined version of the elements being fashioned in Mauritania at the time. This was found to be attributed to the Al Moravid dynasty.
Spatial arrangements and massing of the buildings are derived from architecture of the desert found across the Sahara while the aesthetical treatment attempts to evolve the current architectural elements found across Mauritania in the direction they would have naturally evolved had the Almoravids carried out building works in Mauritania. It is intentionally different from the aesthetics of historic architecture of Morocco as this was the (an austere) style developed and implemented later by the Almohad dynasty that took control of the Maghreb from the Almoravids.


Sustainable Design
With the opportunity to set new benchmarks for sustainable development region-wide the Mauritania Eco Resort, Spa is designed to promote self-sufficiency (particularly related to energy, water and sewerage management), the entire infrastructure will be developed in a manner which sets new standards in ecologically sustainable development in the region.
Like its predecessors, a key aspect of the conservation/ mitigation measures is the protection of indigenous flora and fauna. The presence of wildlife including vulnerable and endangered species within the Banc d’Arguin means that the Mauritania Eco Resort and Spa development aims to incur no negative impacts upon the native fauna population.
And through extensive re-vegetation and rehabilitation program, including the net expansion of potential habitat, establishment of controlled vehicular movement corridors and the protection of site by a 2.9-metre high perimeter fence with 24-hour patrolled entry/exit point, the resort aims to achieve a net positive impact throughout the development.






